Build & deploy a Python app to NOVA
This guide is for experienced developers who prefer working locally. The instructions assume you’re comfortable setting up your environment, installing tools, and deploying software.
NOVA provides a platform to develop, deploy, and manage custom applications for controlling robots. You’ll build locally using the Wandelbots NOVA Python SDK, push your app to a registry, and deploy it to your NOVA instance using the NOVA CLI.
What this guide covers
- Scaffolding a Python app from a template (so you start with a minimal, working server)
- Implementing your app logic and HTTP endpoints
- Containerizing the app with Docker
- Using the Wandelbots CLI to package, and deploy to a cell
- Verifying your app at
/cell/<your-app-name>
If you’re looking for the fastest and easiest path, working on a Wandelbots NOVA cloud instance remains the quickest way to start prototyping. This document focuses on the local workflow and takes you from a template to a running app on NOVA.
Prerequisites
You completed the Wandelbots NOVA quickstart guide and have a NOVA cloud instance running including a robot. The local development setup will interact with this instance.
Set up docker and registries
NOVA applications are deployed as Docker containers. You’ll need Docker installed locally and access to an OCI registry such as Docker Hub.
Install Docker and create account
Install Docker Desktop (or Docker Engine) and create an account on your preferred OCI registry.
Log in to registry
Open your terminal and input the following command. This will allow Docker to push images to your registry:
docker login --username MY-DOCKER-USERNAME MY-REGISTRYIf you’re using Docker Hub, the registry value is typically registry-1.docker.io/MY-DOCKER-USERNAME.
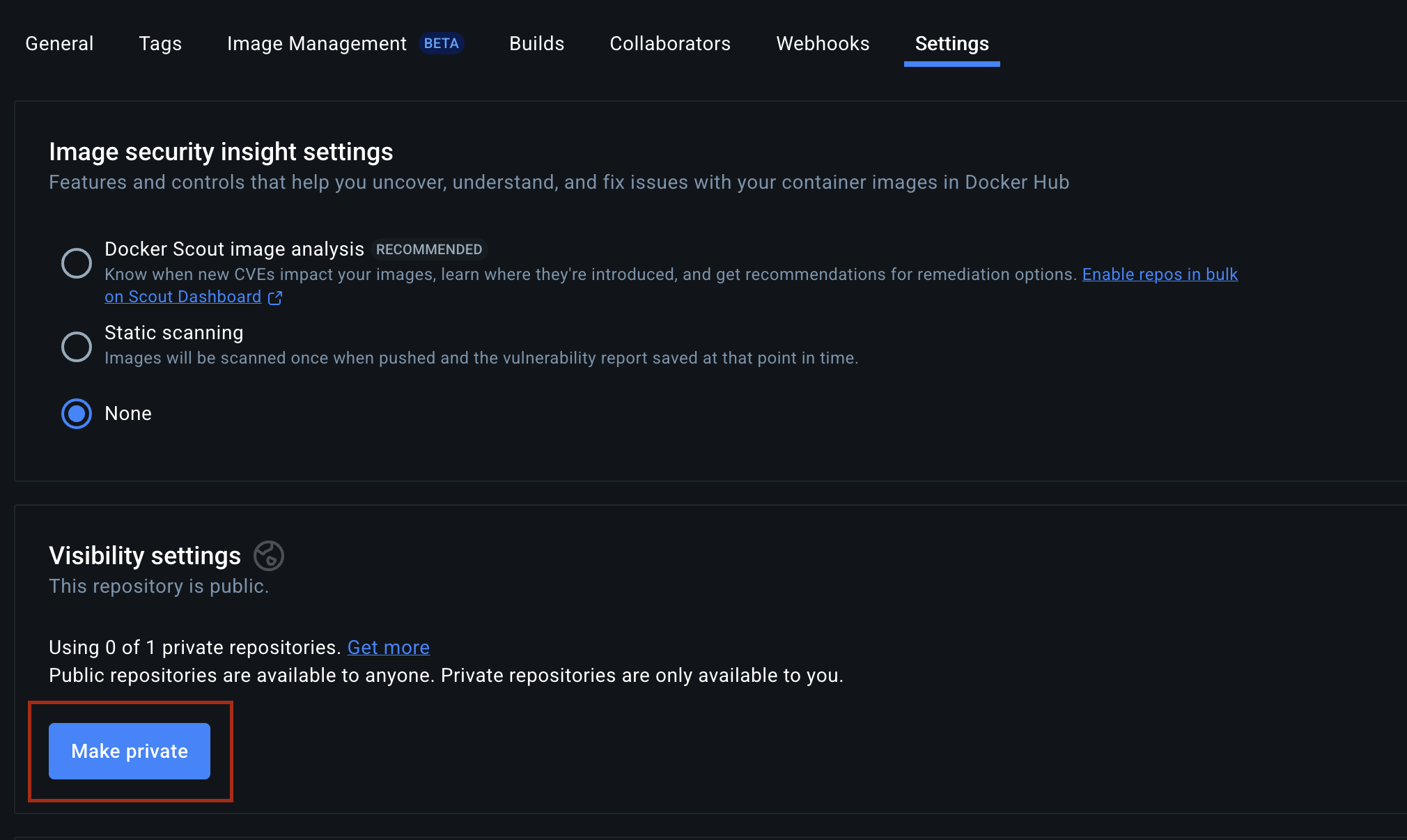
Update repository visibility in Docker
By default, repositories created on Docker Hub are public. If you want to keep your images private, open the repository settings and change the visibility as shown below.
Private repositories ensure that only authenticated users can pull your app image.
Install the NOVA CLI
The NOVA CLI is a command-line tool for creating applications and deploying them to our platform.
It includes many additional features that you can explore on GitHub or after
installation by running nova --help.
macOS/Linux
Install the Wandelbots NOVA CLI tool using Homebrew .
brew install wandelbotsgmbh/wandelbots/novaEnable autocompletion for zsh.
echo 'source <(nova completion zsh)' >> ~/.zshrcTo see all available autocompletion commands for other shell types, run:
nova completion --helpManual installation
Download the Wandelbots NOVA CLI tool and configure it in your local environment.
Rename the downloaded file to nova and make it executable.
Grant the file execution permissions, as the program is not signed.
In order to ensure a smooth process, add the Wandelbots NOVA CLI to your terminal’s path.
The exact process depends on your operating system and terminal.
Set up CLI
Once you have the CLI installed, the first step is to specify the NOVA instance you’re using.
If you don’t specify a host, the CLI will default to using a local instance.
Physical instance or VM
Deploying to a physical controller or virtual machine in your network typically relies on IP connectivity.
Set the host of your NOVA instance:
nova config set host 192.168.1.100Provide additional authentication details if your instance requires them.
Set image registry
If you are not planning to install your app, you can skip this step.
Now, configure the NOVA CLI to specify where to push your Docker images. This registry will also be used by your NOVA instance to pull the images.
nova config set image-registry MY-REGISTRYCreate an application
Now that you have everything installed and configured, let’s create an application.
Create project with Python template
nova app create myappThe CLI creates a standard Python project that uses uv for dependency management and FastAPI for the HTTP interface.
Default FastAPI routes expose your robotics programs without any extra wiring,
and you can extend them whenever you need to customize the API.
Below are some helpful uv commands:
# Create the environment and install dependencies
uv sync
# Add a new dependency
uv add some-packageThe template is optimized for GitHub Copilot and ships with prompts you can reuse:
local_setupchecks local prerequisites and tooling.new_programbootstraps robotics programs that follow the Python SDK patterns.start_serverstarts the development server.test_programruns a selected program.deploy_appwalks you through publishing to NOVA.copilot-instructions.mddocuments the project structure and collaboration tips.
Check the official visual studio code documentation to learn more about this feature.
Copilot accelerates the workflow, but it can also introduce incorrect or overly complex code. Knowing Python fundamentals makes it much easier to review Copilot’s suggestions and catch issues early.
Update .env file
When working with any project you created with NOVA CLI, you need to make sure the .env file is updated. The following information is needed in the .env file:
- NOVA_API: this is your NOVA HOST. If you have an instance from our cloud, you should put xxxxx.instance.wandelbots.io
- CELL_ID: every NOVA application exists in a cell. When you get started, you will have only one cell which is named
cell. - NOVA_ACCESS_TOKEN: This is the access token you can get from our developer portal. Only set this if you are using an instance from the cloud.
- NATS_BROKER: You don’t need this if you are using the cloud, as it is automatically created for you. But if you are using NOVA in an IPC or in a virtual machine, it should be set up like this
ws://IP:80/api/nats
Start app
Start your app by running
uv run python -m myappThen, open the browser and see the API.
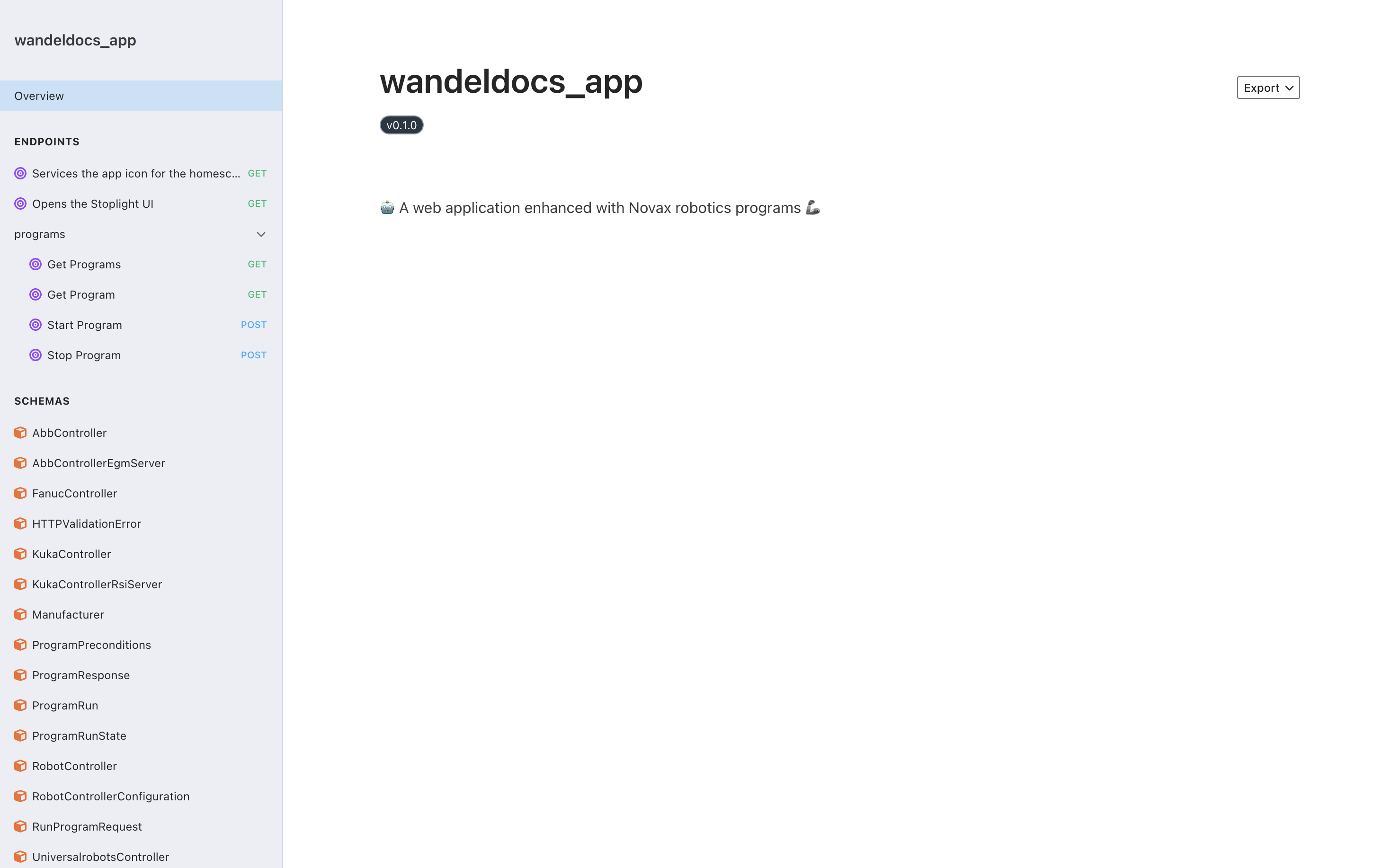
As you can see you got a couple of APIs out of the box. These APIs are integrated to our system and when you write robotic programs they will automatically be integrated with these APIs.
If you want to extend the project no worries. We only register some routes to your API, you still have the full flexibility to implement new APIs and own the FastAPI object.
Deploy app
Now that your app is up and running, you can deploy it by running this command.
nova app install myappVerify app installation
After your app is installed, go to the home screen and make sure the app is visible.

You can customize the icon by changing the app_icon.webp in the auto generated project.
Add custom endpoints to FastAPI
The app template provides default functionality with NOVAx app template however, the FastAPI object lives on user code. This means, you have the full power to customize app layer.
The provided app.py file contains two examples:
App icon
This API returns the image that is used in the home screen for your app:
@app.get("/app_icon.png", summary="Services the app icon for the homescreen")Stoplight API Interface
This API returns an open source project, Stoplight , which provides convenient user interface for working with your APIs:
@app.get("/", summary="Opens the Stoplight UI", response_class=HTMLResponse)Further Steps
To use the full Python SDK capabilities, refer to the Wandelbots Python SDK documentation or by exploring the Python SDK GitHub repository .
To create FastAPI servers that expose robot programs as REST APIs for other frontend frameworks to consume, refer to the NOVAx framework .